Instruments Have Now Been Integrated Into NOAA’s JPSS-1
Building a weather satellite is no easy task—several years of design and engineering work are required to piece all of the instruments together and prepare a satellite for launch.

Ball Aerospace technicians lower the ATMS instrument onto the JPSS-1 spacecraft. Photo is courtesy of Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp.
As NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-1 (JPSS-1) satellite moves towards its early 2017 launch date, the fifth and final instrument, the ATMS (Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder), an instrument critical to forecasting weather three to seven days in advance, has been integrated with the satellite.
“This marks a very significant milestone for the JPSS program,” said Harry Cikanek, JPSS Director. “Soon, the spacecraft will be prepared for the environmental testing phase which is the next step toward launch.”
Historically, microwave sounders, such as ATMS, have had the greatest impact on forecast accuracy.The instrument works by collecting microwave radiation from the Earth’s atmosphere and surface day and night, even through thick clouds.
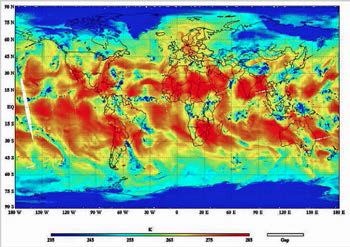
The image shows the ATMS channel 18 data, which measures water vapor in the lower atmosphere. Tropical Storm Sean is visible in the data, as the patch of blue, in the Atlantic off the coast of the Southeastern United States. Image courtesy of NOAA.
This is particularly valuable for forecasters because it will allow them to “see” inside and below clouds, and it can be used to produce images inside hurricanes and other storms. ATMS measurements also provide rainfall rates and snow and ice information.
The image shows the ATMS channel 18 data, which measures water vapor in the lower atmosphere. Tropical Storm Sean is visible in the data, as the patch of blue, in the Atlantic off the coast of the Southeastern United States.
Compared with NOAA’s legacy microwave sounders, ATMS offers more channels and better resolution and collects a wider swath of data. ATMS will be operating in tandem with CrIS (Cross-track Infrared Sounder) aboard the JPSS-1 satellite.
By working together to cover more of the electromagnetic spectrum (microwave and infrared), ATMS and CrIS will provide coverage of a broad range of weather conditions.
“The JPSS-1 ATMS sensor will guarantee that this critical data stream remains seamlessly in place to support global forecasting in the future,” said James Yoe, Ph.D., NOAA’s National Weather Service.
ATMS is built by Northrop Grumman in Azusa, California, and was delivered to Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colorado, where it was integrated with the spacecraft. ATMS currently flies on the NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP satellite mission and will fly on the JPSS-1, JPSS-2, JPSS-3, and JPSS-4 satellite missions.
SpeedCast’s Beylier Named As 2016 Teleport Exec. Of The Year By The WTA
The World Teleport Association (WTA) has announced that Pierre-Jean Beylier, the CEO of SpeedCast, has been named as its 2016 Teleport Executive of the Year.

Mr. Beylier will be honored during WTA’s Teleport Awards for Excellence luncheon on March 8 during SATELLITE 2016, hosted by Crystal.
The Teleport Executive of the Year award is presented to an individual for demonstrated entrepreneurship, leadership and innovation in the development or operation of a teleport-based business. Under the leadership of Pierre-Jean Beylier, known as PJ, SpeedCast executed five acquisitions in 2015, which doubled the company’s revenue, while achieving 99 percent retention of the staff in the acquired companies.
This remarkable performance stems from corporate values summed up in the acronym “CAST”—Customer-focused, Agile and responsive, Success through people and Team spirit. The work of integration these acquisitions is called Project Bordeaux, whose goal is to turn six companies into one streamlined and efficient organization. Project Bordeaux stresses communication: giving all team members visibility into what the organization is doing, what it has achieved and what is coming next. The result has been increasing cross-team collaboration leading to a higher “win” ratio and faster project delivery.
PJ also leads the company’s engagement with humanitarian and charitable organizations. The company has contributed equipment and technical support under the NetHope initiative for recovery from Hurricane Haiyan. SpeedCast is a corporate supporter of charitable events including Australia’s Big Red Ride, which raises money for muscular dystrophy research, World Championship Sailing in Japan, and other events. With its focus on nonprofit organizations, SpeedCast is also a major supplier to such NGOs as UNHCR, UHHDOC and Save the Children International. From his base in Hong Kong, PJ has built a company with global reach across the mobile, maritime, energy, government, mining and NGO markets.
“A healthy technology sector offers opportunities to small, entrepreneurial companies as well as to mid-size and large firms with the potential to acquire them,” said executive director Robert Bell. “The teleport industry is just such a sector and executives like PJ Beylier not only build on the success of the companies they acquire but increase the potential of the industry for growth.”
And The Beat Goes On... The Intelsat 29e Push
Launched from the Arianespace’s European spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, flight number 228 successfully placed the Intelsat 29e telecommunications satellite in geostationary transfer orbit.

Flight VA228 was the 84th launch for Arianespace’s Ariane 5, which operates from French Guiana. Photo courtesy of Arianespace.
This was the seventh launch of an Ariane 5 with Airbus Safran Launchers as lead contractor, in coordination with the teams from the respective parent companies, Airbus Defence and Space, and Safran.
Airbus Safran Launchers demonstrated, with Arianespace, the ability to respond to the specific needs of one of its clients in record time, as the launcher was adapted to accommodate a single satellite rather than the customary two satellites for which Ariane 5 ECA has been optimized. Launch performance was 6700 kg (of which 6552 kg was the actual satellite) to geostationary transfer orbit with an inclination of 0.5 degrees, thereby optimizing the lifetime of the satellite.
“Following the year 2015 with 6 successful launches in 7 months, 2016 starts with a demonstration of our ability to adapt, thanks to the engagement of the teams and the operational flexibility of the industrial organization,” Alain Charmeau, CEO of Airbus Safran Launchers pointed out. “This level of flexibility is made possible by the expertise and know-how of the teams at Airbus Safran Launchers and its parent companies. This first success of 2016 marks the beginning of a series of operational challenges for Ariane 5 over the coming year. I would like to thank the European Space Agency, CNES and Arianespace for their confidence.”
Airbus Safran Launchers has been the prime contractor for the Ariane 5 European launcher, one of the largest and most ambitious space programs in the world, since January 2015.
Building on the expertise of the Airbus and Safran groups, the company oversees an industrial network that brings together more than 550 companies (more than 20 percent of which are SMEs) in 12 European countries.
Airbus Safran Launchers manages the entire industrial supply chain, from the manufacture of equipment and stages to the complete integration of the launcher in French Guiana, in line with the customer’s specifications.
Representing cutting-edge European expertise, the Ariane 5 launcher has been specially designed to inject heavy payloads into low Earth orbit or 2 satellites into geostationary transfer orbit.
Airbus Safran Launchers is also the prime contractor for the future European launcher Ariane 6, whose maiden flight is scheduled for 2020.
PJ also leads the company’s engagement with humanitarian and charitable organizations. The company has contributed equipment and technical support under the NetHope initiative for recovery from Hurricane Haiyan. SpeedCast is a corporate supporter of charitable events including Australia’s Big Red Ride, which raises money for muscular dystrophy research, World Championship Sailing in Japan, and other events. With its focus on nonprofit organizations, SpeedCast is also a major supplier to such NGOs as UNHCR, UHHDOC and Save the Children International. From his base in Hong Kong, PJ has built a company with global reach across the mobile, maritime, energy, government, mining and NGO markets.
Aerojet Rocketdyne Support For The Intelsat 29e Launch
Rocket engines made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, a subsidiary of Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc., are now providing in-flight maneuvers for the Intelsat 29e communications satellite, which launched aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana on January 27.
Boeing Satellite Systems International, which built the Intelsat 29e satellite, has also announced that the spacecraft is now fully operational.
“Aerojet Rocketdyne is thrilled to be a part of another successful satellite program for Boeing, as well as part of another successful Intelsat mission,” said Ron Felix, vice president of the Space Systems Business Unit at Aerojet Rocketdyne. “Aerojet Rocketdyne has rocket propulsion products on every one of the 50+ operational Intelsat satellites located around the globe, and we look forward to continuing that tradition.”
Aerojet Rocketdyne propulsion included 16 rocket engines on the satellite: 12 four-Newton MR-111C hydrazine and four 22-Newton MR-106L hydrazine engines, all of which provide attitude control and adjustment, east-west station-keeping, spin control, decommissioning and settling burns.
The MR-111 and MR-106 engines have extensive flight history, each having flown on more than 2,000 missions with 100 percent mission success.
Intelsat 29e is the first of six Intelsat EpicNG satellites being built by Boeing. Intelsat EpicNG is a high performance, next generation satellite platform that delivers global high-throughput capability.

The next four Intelsat EpicNG satellites, also being built by Boeing, will include six Aerojet Rocketdyne electric propulsion thrusters for north-south station-keeping, in addition to the 16 hydrazine rocket engines.
The electric propulsion system provided by Aerojet Rocketdyne for each of the four remaining Intelsat EpicNG satellites includes a 4.4kW power processing unit, electrical harnessing and four 2.2kW MR-510 electric arcjet thrusters.
Aerojet Rocketdyne has flown more than 170 MR-510 arcjet thrusters with 100 percent mission success. The MR-510 arcjet provides fuel-efficiency performance that is three times better than the MR-111 and MR-106 hydrazine
rocket engines.
arianespace.com/
rocket.com/
boeing.com/
Off + Away With Sentinel-3A
The first of the two flight models of the Sentinel-3 satellites—Sentinel-3A, primed by Thales Alenia Space—was launched on February 16 via a Rockot launcher, from the Plesetsk cosmodrome in Russia.

A Rockot launcher drives Sentinel-3A to orbit.
Sentinel-3A is the size of a small car with a mass of 1150 kg and is designed for an operating life of seven years.
On board Sentinel-3A is an Airbus Defence and Space-built microwave radiometer (MWR) used to remove signal errors caused by water vapor in the atmosphere.
This allows accurate tracking over a variety of watery surfaces: open ocean, coastal sea zones, sea ice and inland waters.
The 26 kg radiometer measures the thermal radiation emitted by Earth, enabling signal delays caused by moisture in the troposphere to be added to the altimeter pulses, to deliver more accurate data.

MWR photo is courtesy of Airbus Defence & Space.
Airbus Defence and Space was also responsible for the thermal architecture of the service and payload interface module, which will ensure the correct performance under the extreme temperature variations to which the satellite will be subjected once in orbit, and acryo-cooler system for the Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR) instrument.
The Sentinel-3 mission is specifically designed to ensure long-term collection and operational delivery of high-quality measurements for ocean, land and atmospheric services.
The satellites build upon the heritage and data from the Airbus-built missions of ERS,Envisat and SPOT, and include enhancements to meet the operational revisit requirements and to facilitate new products and an evolution of services.
The satellite will extend observations to inland waters and coastal zones.
The primary application of the Sentinel-3 mission is to monitor the world’s oceans, measuring the temperature, color and height of the sea surface and the thickness of sea ice.
The data produced will allow scientists to monitor sea-level change and sea-surface temperature, manage water quality, track marine pollution and biological productivity.

Artistic rendition of the Sentinel-3A satellite on orbit. Image is courtesy of ESA, Pierre Carril.
Sentinel-3 will also provide a land-monitoring service with wildfire detection, land-cover mapping and vegetation health monitoring, providing complementary data to the multispectral optical mission of Sentinel-2.
Eurockot Launch Services GmbH is the Bremen, Germany, based joint venture of Airbus Safran Launchers and Space Center Khrunichev.
In addition to the Sentinel-3A launch Eurockot will orbit two more satellites for Europe´s Copernicus program.
After this successful launch of Sentinel-3A, EUMETSAT is now preparing to exploit the Copernicus satellite on behalf of the European Union, in cooperation with ESA.
Under the Copernicus agreement it signed with the European Commission on November 7, 2014, EUMETSAT will be the operator of the Sentinel-3A satellite and will deliver its marine mission on behalf of the European Union, in cooperation with ESA.
EUMETSAT will take over operations of the Sentinel-3A spacecraft in five months from now, upon completion of the ESA-led, in-orbit commission phase, and will process Sentinel- 3 marine data and products at its Sentinel-3 Marine Centre for real time delivery to the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service and end-users.
Sentinel-3 is the second of five Copernicus missions to be operated by EUMETSAT, the first being the cooperative Jason-3 marine and climate mission launched on January 17 of
this year.
Arianespace Signs On To Launch New ViaSat Satellites
Arianespace and ViaSat Inc. (NASDAQ: VSAT) have contracted for the launches of ViaSat-2 and a ViaSat-3 class satellite.

Artistic rendition of the ViaSat-2 satellite. Image is courtesy of ViaSat and Boeing.
Both ViaSat-2 and ViaSat-3 class satellites are geostationary satellites and operate in the high capacity Ka-band frequencies.
ViaSat-2 and ViaSat-3 will each weigh approximately 6,400 kg at launch and will be injected into geostationary transfer orbit by the Ariane 5 ECA, respectively, during the first quarter of 2017 and by late 2019/early 2020.
Boeing Satellite Systems in El Segundo, California, is the build partner on both satellites.
These launches will take place at the Guiana Space Center, Europe’s Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana.
ViaSat is focused on providing affordable, global, high-speed broadband Internet with competitive advantages on the ground, in the air, and at sea—as compared to other satellite and terrestrial alternatives.
The ViaSat-2 satellite system is expected to improve speeds significantly, reduce costs and expand the footprint of broadband services across North America, Central America, the Caribbean, a portion of northern South America as well as the primary aeronautical and maritime routes across the Atlantic Ocean between North America and Europe.
The satellite will offer approximately double the bandwidth of ViaSat’s previous generation satellite, and seven times the coverage.
An ultra-high capacity satellite platform, ViaSat-3 comprises three ViaSat-3 class satellites plus advanced state-of-the-art ground network infrastructure, enabling the first truly global high-speed broadband service.
Each ViaSat-3 class satellite will offer more than 1,000 Gigabits per second (Gbps) or 1-Terabit per second (Tbps) - of bandwidth to enable high-speed Internet, including video streaming, at scale across multiple applications simultaneously.
The first ViaSat-3 satellite system will address the Americas, followed by a second satellite system serving Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) and a third system planned for the Asia Pacific region.
The ViaSat-3 satellite platform is expected to deliver unprecedented coverage, capacity, cost, service and flexibility.
Mark Dankberg, ViaSat’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, said, “We have a long-standing relationship with Arianespace, and have committed to launch two ViaSat satellites in the next four years with them. By partnering with Arianespace on ViaSat-2, we build confidence in our plan to bring new high-speed service plans across the U.S. and the region by the middle of 2017.
“These service plans are made possible with the innovative technologies underlying the ViaSat-2 network. Beyond ViaSat-2, we plan to launch a ViaSat-3 class satellite with Arianespace, where we will offer our customers even higher speeds and higher quality broadband services—ranging from faster home Internet services and in-flight video streaming to high-speed, high-value connectivity for government aircraft missions.
“These two satellite launches are key in the evolution to bring a global broadband communications network to market that delivers affordable, high-speed Internet access to all.”
Arianespace Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Stéphane Israël, said, “Arianespace is proud to be entrusted with the launches of ViaSat-2 and one ViaSat-3 class satellite, and thus be given the opportunity to contribute to the implementation of space-based solutions for global connectivity. I thus want to express my gratitude to ViaSat for its confidence and for involving Arianespace in the development of its broadband communications network. With this contract, Ariane 5, which completed last month its 70th successful mission in a row, is confirmed as the reference launch vehicle selected by most private satellite operators worldwide.”
viasat.com
arianespace.com
www.boeing.com
Coming In March... NSR’s 10th Wireless Backhaul Via Satellite Analysis
NSR’s Wireless Backhaul via Satellite, 10th Edition is the longest-standing industry analysis and forecast of the satellite Internet and telephony backbone sector—the study includes 3 key segments:
• Mobile Backhaul
• Internet & Telephony Trunking
• IP Content Distribution (NEW FOR 10th Edition)
The assessment covers the installed base of sites in seven regional markets, investigates trends impacting market growth and business models, forecasts capacity requirements and equipment shipments, and calculates satellite capacity and CPE revenues. The main issues and questions addressed in the study include:
• What are the trends driving or restraining growth in the installed base for each market vertical
and region?
• How is HTS expanding the addressable market in all verticals, and how are Business Models evolving for Service Providers, Equipment Vendors and Satellite Operators?
• How are market elasticity and the downward trend in pricing creating new demand and opening new markets?
• What is the addressable market, and what are the opportunities in each region?
• What are the technology trends shaping the industry, and how is demand for 2G/3G/4G services evolving in each region?
• What are the implications of bandwidth-hungry sites in the battle of frequencies and architectures? What is the satellite capacity demand for each service in each region, and how is this being provisioned?
• With Video and Media consuming most of the IP Traffic, can satellites enter the IP Content Distribution market serving CDNs, Video Offload and other opportunities?
• What are the revenues to be generated from capacity provisioning and customer premises equipment (CPE) sales in each region and market vertical?
Widebeam C-, Ku- and Ka-band coverage together with an HTS breakout into C-band, Ku-band, Ka-band and non-GEO HTS is now a standard part of this report. In addition, for the Mobile Backhaul section, this study includes a comparison of backhaul technologies (terrestrial and satellite), a series of financial models comparing different satellite architectures and base station technologies, and a section assessing the addressable market both in terms of total mobile base stations and the opportunities to extend network coverage.
Gilat’s Satellite Backhaul Brings High-Speed LTE Services To SoftBank

SoftBank Corp. (“SoftBank”), a subsidiary of SoftBank Group Corp. providing mobile communication, fixed-line communication and Internet connection services to customers in Japan, and Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd., a provider in satellite networking technology, satellite mobility solutions and services, have announced that SoftBank intends to provide high-speed LTE services using Gilat’s satellite-based cellular backhaul technology following a successful field trial.
This technology makes it possible for SoftBank to cost-effectively offer high-speed mobile communication services in remote areas where it is difficult to install fixed-line facilities and base stations. SoftBank expects to offer commercial services in Japan, based on this technology, within 2016.

SoftBank has already succeeded in providing cost-efficient 3G mobile communications in Japan, where it is difficult to build facilities for fixed-line and mobile communications, by using satellite communications as backhaul. SoftBank contributed to the development of Gilat’s SkyEdge II-c high-speed satellite communications platform early on, and conducted verification work along the way. The latest trials demonstrated FTP downlink rates of up to 100Mbps using actual mobile handsets, which until now have been very difficult to achieve.
Yasuyuki Imai, SoftBank’s Executive Vice President and Head of the Technology Unit, said, “With this technology, we will be able to also offer high-speed LTE services in mountainous regions, remote islands and other areas in Japan where it is difficult to install fixed-line backhaul cost-effectively and quickly. We already have satellite-based backhaul in those regions, but now we will be able to offer our customers LTE speeds. We also expect to see the application of this technology to the mobile network of our group company Sprint in the US. Our hope is that this technology will help play a role in bridging the digital divide.”
Dov Baharav, Gilat’s Chairman of the Board and Interim CEO, said, “Gilat is the pioneer in delivering 4G satellite-based cellular backhaul for mobile network operators and our new technology allows for quick time to market and complete 4G service.”
Hughes Mines Point-To-Point Satellite Links For MSHA Mine Emergency Operations
Hughes Network Systems, LLC has completed implementation of a managed enterprise network for the US Department of Labor’s Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA).
The program is delivering remote connectivity to MSHA Mine Emergency Operation’s (MEO’s) vehicles and facilities across the country, further enhancing the agency’s broadband capacity and communications infrastructure.
The contract has a ceiling value of approximately $1.36 million over the course of one year plus four option years.
Under the program, Hughes is providing point-to-point satellite links for mobile site-to-site communications that satisfies low latency requirements for MSHA’s high-priority network traffic/applications.
In addition, Hughes is providing access through an enterprise network comprised of point-to-point connections between the IP Gateway at the Hughes Network Operations Center and MSHA’s data center. This solution delivers MSHA its requisite Internet connection speeds (3,072Kbps down/1,024 Kbps up), allowing it to deploy small private networks more economically and eliminating the need for a backhaul.
Other contracted deliverables provided by Hughes include:
• Project planning and implementation scheduling
• Coordination of overall site installation process
• Implementation of site maintenance plan
• Reporting and project status reviews
• Ongoing operations and support management
“As the world’s leading satellite broadband provider, Hughes is in a unique position to satisfy MSHA’s enterprise network requirements, especially as it relates to mobile and remote connectivity solutions,” said Tony Bardo, assistant vice president of Government Solutions at Hughes. “The equipment and services under our HughesON™ suite of managed services will greatly increase the mobility of MSHA’s personnel and help facilitate their mission to improve the safety of our nation’s mines.”