SpeedCast + Gazprom Partner To Address Africa’s Energy Sector Comms
SpeedCast International Limited (“SpeedCast”) has announced a new agreement with Gazprom Space Systems (“GSS”), a Russian-based satellite operator, to expand satellite communications services in Africa.

This partnership allows SpeedCast to access capacity on GSS’s Yamal-402 Ku-band satellite to provide high-performance services to global oil and gas companies across Africa.
With the uplink based in Germany, customers will be able to land their traffic directly into Europe, taking advantage of high-speed interconnection throughout Europe.
Further, Germany’s excellent standards of infrastructure and advanced data security laws will ensure the highest levels of security for customers’ sensitive data.
“We are always searching for the best solutions for our customers in the key countries in which they operate,” said Moti Shulman, Vice President, Technologies & Network Planning, SpeedCast International Limited.
“The expansion of our services for the African resource market augment SpeedCast’s current service capacity in Africa. We are thrilled to partner with Gazprom Space Systems to deliver communication services into the African region. Delivering innovative solutions to meet the needs of our customers is at the heart of our success.”
Dmirty Sevastiyanov, Director General, Gazprom Space Systems, said, “Our partnership with SpeedCast will further strengthen our common ability to deliver the reliable and efficient broadband and mobile connectivity that energy companies demand today.”
GVF To Spotlight SATCOM Mobility
In response to escalating demand for satellite-based solutions—as well as challenges posed by new user requirements—the Global VSAT Forum (GVF) will launch the Applied Innovation Conference.
The industry event, which will be hosted by Intelsat at their Washington, D.C. offices, will examine new technology solutions applied through space segment, Earth station equipment, networking, and delivery of satellite communications and broadcasting.
“The conference will present a unique opportunity for the technical community, at all levels of the supply chain, to achieve peer-reviewed recognition for innovation, to network with colleagues, and to better understand the real-world needs of the market,” said David Hartshorn, Secretary General, GVF.
The theme for the first Applied Innovation Conference will be “Satcom Mobility: Challenges and Solutions”. In preparation for the event, GVF has established a peer-review Technical Committee and is inviting submissions related to antennas; amplifiers; modulation and coding; acceleration; bandwidth management; constellations; interference management; payloads; propagation effect mitigation; fixed, COTP, and COTM terminals; user interfaces; human factors; and cost reduction. Developments that support interference prevention will be given a high priority in the Technical Committee’s selection process.
Authors of selected papers will be invited to present their work in a session or in poster format in the Conference exhibition area. Sessions will include panels of end users, operators, and service providers with presentations of accepted technical papers. The panel, authors, and audience will have a unique opportunity to interact and develop new understandings of technological solutions to real-world industry needs. Accepted papers will be published in open-access, online proceedings. For further details, including submission deadlines and other instructions for authors, contact the Technical Chair.
To register and reserve your seat, and to inquire regarding sponsorship opportunities and exhibit space, contact Angie.Mar@gvf.
A New Generation Debuts From NovelSat
NovelSat, a provider in satellite transmission technology, has released NovelSat NS4, the company’s 4th generation satellite transmission waveform, for general availability.
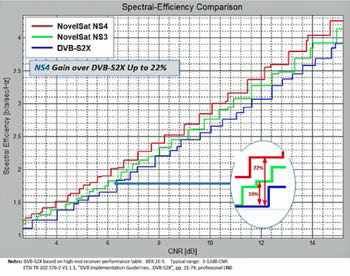
In head-to-head demonstrations, NovelSat has shown that NovelSat NS4 delivers up to 22 percent higher spectral efficiency compared with DVB-S2X, the industry’s current satellite transmission standard.
NovelSat NS4 is now available as an optional software package in all NovelSat satellite modems, modulators and demodulators, which also support and are backward compatible with all industry specifications.
For the satellite communications industry, that extra boost of spectral efficiency with NovelSat NS4 means more HD and
4K UHDTV channels and more data without increasing their costly satellite bandwidth budgets.
For those with steady satellite bandwidth needs, as much as 22 percent better efficiency means they can transmit the same content using far less bandwidth.
In networks using the DVB-S2 standard, switching to NovelSat NS4 can boost capacity by up to 45 percent without increasing bandwidth.
The new NovelSat NS4 waveform, like all NovelSat features, is a software upgradable option that can be installed over the air (OTA) on all NovelSat satellite devices.
This software-only model has proven very popular with NovelSat customers who want to optimize bandwidth utilization without the hassle or cost of replacing equipment.
“Since we released NovelSat NS3 in 2011, NovelSat has consistently offered our customers the most bandwidth efficient satellite technologies available,” said Itzik Wulkan, NovelSat CEO.
“NovelSat NS4 is a technological breakthrough which is the culmination of years of experience and hard work that started the day after NovelSat NS3 was released.”
Along with NovelSat NS4, NovelSat released the NovelSat NS4 Calculator. This is a tool that can be used, upon request, to show details about how NovelSat NS4 optimizes bandwidth usage with varying operating parameters.

NovelSat also recently announced a new streamlined customer support program which, among its other advantages, offers Gold-level customers eligibility for free upgrade paths to NovelSat NS4.
NovelSat first demonstrated the competitive advantages of NovelSat NS4 at the Satellite 2015 Exhibition.
Next week, NovelSat is inviting broadcasters, satellite communications providers, users and integrators to see NovelSat NS4 demos at the Satellite 2016 show, March 8-10 at National Harbor, Maryland.
* DVB-S2X support available Q2-2016.
novelsat.com/
SapphireBlu™ SSPA/SSPB Enters Market From Advantech Wireless
Advantech Wireless has debuted a new, significant advance in solid state power amplifier (SSPA) technology with the release of its SapphireBlu™ Solid State Power Amplifier/Power Block (SSPA/SSPB), based on second generation Gallium Nitride (GaN) technology.
The new system is designed to service new satellites operating in the 12.75 to 13.25 GHz band.
This small form factor SSPA is designed to be hub mounted very close to the antenna’s flange input, eliminating losses through a waveguide, which will now make it possible for a relatively small SSPA—alone—to transmit the signal.
Because of this efficiency, air conditioned shelters for a Klystron or indoor mounted HPA can be eliminated. Instead of needing multiple antennas at a teleport, operators can reduce their number, simplifying operations at each teleport.
Further, the unit operates as 1:1 redundant or 1+1 phase combined, to provide additional power when traffic demands, and the unit has a built-in L-band interface Back-Up Converter without separate up converters.
The SSPA units are very power efficient, reducing operational expenses for power consumption, and capital expenses from reducing the need for uninterruptible power sizing. This enables a more resilient system for operators at no additional cost.
Cristi Damian, VP Business Development at Advantech Wireless, said, “This new technology is designed to replace multiple older technology klystrons or Traveling Wave Tubes (TWTs), with more resilient technology, much simpler hardware configuration on site, and a considerable reduction in operating expenses.”
Visit the Advantech Wireless Booth 717 during the Satellite 2016 Conference and Exhibition, occurring from March 7th through March 10th at the Gaylord National Convention Center, National Harbor, Maryland.
advantechwireless.com/
Hiltron Just In Time... Summer Games Delivery Via DBS Satellite Link
Hiltron announces a satellite link will be used to carry broadcast television content from South America to viewers in Europe.

The new system will be located in one of the Baltic states and will be live by the end of June in time for the 2016 Summer Games in Rio
de Janeiro.
“The new link will be a complete turnkey solution with five active channels and is designed to operate as a complete backup system which can be switched into action if the primary feed fails,” said Hiltron Managing Director Jan Molter.
Core elements of the new system include a 3.6 meter diameter satellite dish on a Hiltron HMAM motorized antenna mount. HMAM is a high-precision motorized satellite antenna mount designed for two-way VSAT communication or receive-only downlink applications. The combined head and drives form a three-axis motorized mount with 180 degrees of azimuth adjustment, 90 degrees of elevation adjustment range and fully adjustable polarization.
Client-supplied solid state power amplifiers and upconverters will be integrated with a Hiltron HACU antenna control unit. This and its associated motor-control electronics are contained in a weatherproof outdoor housing.
The HACU can be operated from a PC running a graphic user interface compatible with standard web browsers.
The control GUI displays all the information required to set and maintain azimuth, elevation and polarization, including current and target positions plus a database of potential accessible satellites.
Also integral to the system will be a Hiltron HDCU-E combined ice-sensing and dish heating controller.
hiltron.de/
An Expansion Is In The Works For North Telecom
North Telecom is going to be expanding their facilities.

“This brings the North Telecom facility and extends the firm’s reach to APAC. The company will now be able to bridge east to west and will be able to offer more cutting edge service and solution to global market,“ said Mahdi Nazari Mehrabi, Managing Director Asia and CTO North Telecom.
“We are investing in this new facility and additional capacity in Singapore to serve the APAC region, these investment will allow NorthTelecom to extend its leading edge and forefront solution and services into Asia and Pacific market in the coming month,” Mehrabi added.
The new facility will be equipped with state of the art ground equipment as well as a highly qualified and competence team on the ground.
North Telecom is a global satellite service provider that provisions satellite communications and ICT services on land and at sea.
Having high-quality managed network services from east to west, North Telecom is delivering leading edge satellite communication services and solution to meet our customer demand all across the spectrum.
Present in 12 international points of presence and 7 teleport operations, as well as serving to more than 100 partners across the globe, North Telecom is enabling business to reach their customers worldwide.
Information regarding North Telecon’s fleet access is available at: northtelecom.com/fleet
Berliner Glass Group Has Optical Systems In Space
The EDRS-A satellite was successfully launched into orbit and the “first section” of the SpaceDataHighway has now been built.
On January 29, 2016, at 23:20 CET, the payload EDRS-A on board the communications satellite Eutelsat 9B was launched into space by a Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome. The satellite has already reached its position in geostationary Earth Orbit, that location being 9 degrees East.
EDRS-A is the first element of the European Data Relay System (EDRS). This system will ensure that low-orbiting satellites will be able to send their information to Earth in near-real time. EDRS-A is equipped with a laser communication terminal (LCT) that was developed and manufactured by Tesat-Spacecom GmbH & Co. KG based in Backnang, near Stuttgart, in Germany.
This laser communication terminal contains several optical components and systems manufactured by the Berliner Glas Group. Optical communication allows enormously increasing amounts of data to be made available in a faster, more reliable way to customers.
In order to exploit the advantages of data transmission with laser light, very sophisticated technologies have been developed and qualified for use in space. Copernicus, the European Program for monitoring the Earth, will be the first user of the SpaceDataHighway. Copernicus’ satellites Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2A that already are located in low Earth Orbit are also equipped with laser communication terminals. Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2A will soon transmit their data to EDRS-A via laser. EDRS-A then will send the information directly to Earth.
The optical components and systems manufactured by the Berliner Glas Group are important elements of the laser communication terminals. The European Data Relay System will enable round-the-clock exchange of large volumes of data between satellites. This will significantly improve Earth observation performance as well as reduce emergency response times.
EDRS-C, the second geostationary satellite of the European Data Relay System, will be launched into orbit on board an Ariane 5 rocket. With EDRS-C, the second section of the SpaceDataHighway will be built. Its orbital position will be 31 degrees East.
edrsspacedatahighway.com
berlinerglas.com/home
NOAA’s Jason-3 Reaches Final Orbit
Following a series of nine orbital maneuvers, executed over several days by the CNES team in Toulouse, France, Jason-3 has reached its final orbit—traveling 348 miles and only one minute and 20 seconds behind Jason-2.

Now that the satellites are flying in tandem formation, the calibration and validation of Jason-3’s data can begin.
Jason-3, a US.-European satellite mission, lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on January 17, 2016, at 10:42 a.m. PST aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket to become the latest spacecraft to track the rate of global sea-level rise.
Jason-3 will also help NOAA’s National Weather Service more accurately forecast the strength of tropical cyclones that threaten America’s coasts.
While flying in a low orbit 830 miles above the Earth, Jason-3 will use a radar altimeter instrument to monitor 95 percent of the world’s ice-free oceans every 10 days.
Since the Topex/Poseidon, and Jason satellite missions started in 1992, researchers have observed global sea-level rise occurring at a rate of 3 mm a year, resulting in a total change of 70 mm—or 2.8 inches—in 23 years.
This successful launch was a major accomplishment for the Jason mission, but it is by no means the end of the road. On the contrary, much of the hard work has just started.
Satellite instruments and the data they provide are incredibly precise. Once operational, the Jason-3 satellite will be able to detect changes in sea level height down to the millimeter. This requires a careful fine-tuning of the instruments from here on Earth.
Once they reach space, satellites are put through a “commissioning phase” that usually lasts a few months.

The launch of Jason-3 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle. Photo is courtesy of SpaceX.
During this phase, the teams check each of the satellite’s systems to make sure they are working properly.
They will also evaluate the accuracy of the data coming from the satellite and make sure that the instruments it carries are properly calibrated.
Once all systems are checked out and deemed operational, the satellite will be moved into its final destination orbit.
Three days after Jason-3 launched, NOAA’s partners at CNES began to acquire and process real-time data from the satellite.
NOAA and CNES will continue to calibrate and validate the instruments and data while EUMETSAT conducts processing trials of the data received at the Usingen ground station
Once this six month phase is complete, Jason-3 will officially begin operations in its planned orbit.
These highly detailed measurements of sea surface height, a measurement used to study sea level rise, are a critical factor in understanding Earth’s dynamic climate.
Sea surface height data are also used to study hurricane intensity, tsunami dynamics, El Niño Southern Oscillation, eddy dynamics, ocean boundary currents, coastal and shallow water tides, as well as weather and climate forecasting.
nesdis.noaa.gov/jason-3/mission.html





